【深度学习】医学图像处理之视杯视盘分割数据集和评价指标

@[toc]
1 数据集(公开)
2.1 视盘标签
ORIGA-650 这批数据集归属于新加坡国家眼科中心,主要包含650张彩色眼底图像,每张图像都有视盘和视杯的分割标注,同时还有是否患有青光眼的诊断标注。拥有这批数据的IMED团队,也是目前国内最大的眼科医疗图像组。 ORIGA-650分为两个子集 set A for training 和 set B for testing 每个子集包含了325张图像。 Messidor Messidor数据集原本是用来做糖尿病视网膜(diabetic retinopathy, DR)病变检测的,只有糖网的分级标注。后来国外的一个课题组又重新手工标定了视盘的边界,因此目前大家也同样在Messidor数据上做视盘的定位和分割。 RIM-ONE RIM-ONE一共发布了三个子数据集(RIM-ONE-R1,R2,R3),他们的数量分别是169,455和159张。 DRION-DB DRION-DB 做的人特别少,但是这批数据集也有111张图像。大家也可以做一下,就当作一种data augmentation了吧。
2.2 视杯视盘标签
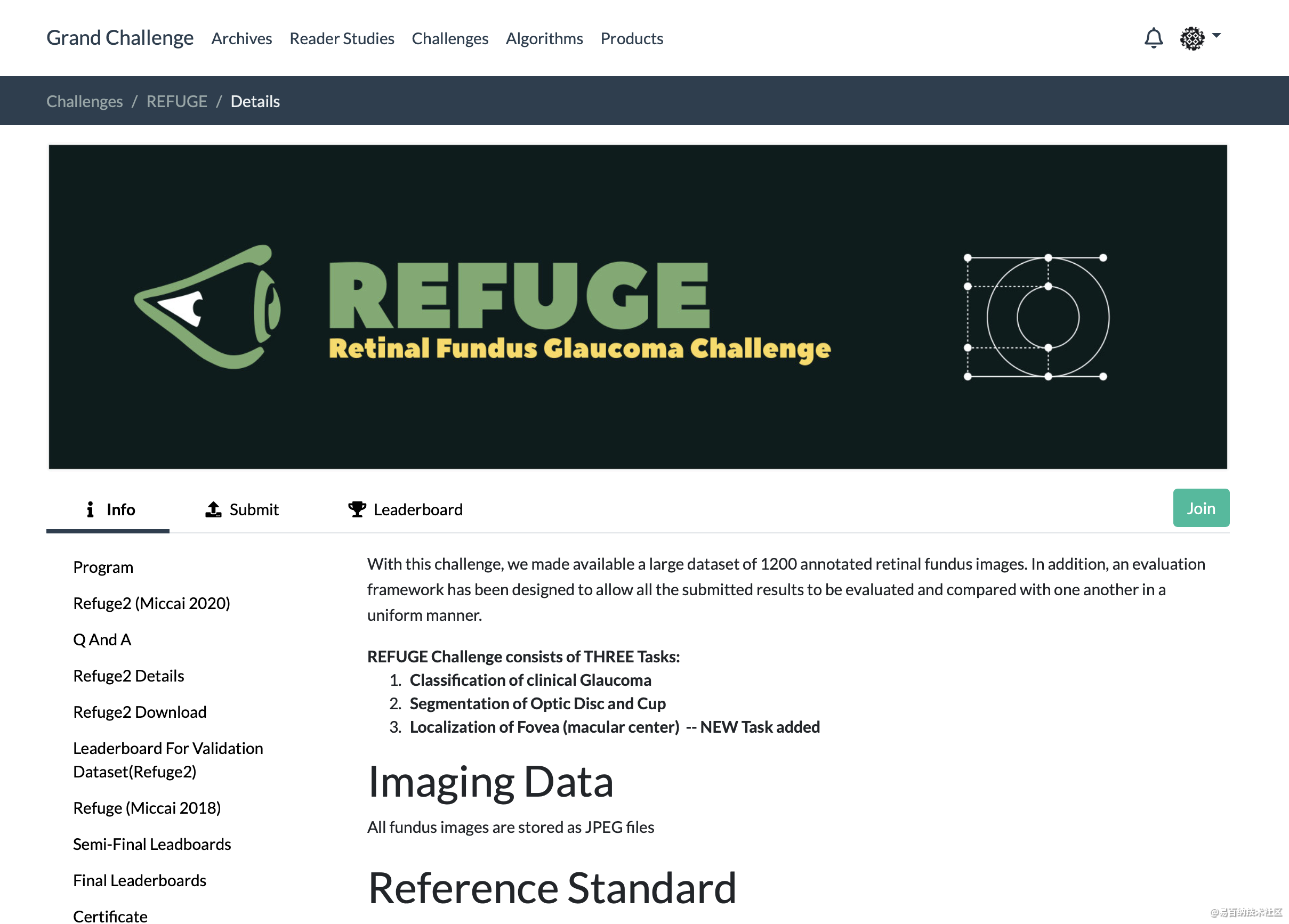
除了上图常用的Refuge数据集外,最近比较新的是GAMMA数据集。 来源于下面的竞赛:
MICCAI2021 Contest : GAMMA 数据简介Dataset Introduction
GAMMA提供的数据集由中国广州中山大学中山眼科中心提供,数据集中包含300个两种临床模态影像的数据对。两种模态分别是临床眼底检查常做的2D眼底彩照和3D光学相干断层扫描(Optical Coherence Tomography, OCT)。我们将各类别数据三等分,分别为训练过程、预赛过程和决赛过程准备了100个数据对。对于深度学习算法,100个训练数据对属于小样本,我们鼓励参赛者提出适用于小样本数据集训练的模型。
The dataset released by GAMMA was provided by Sun Yat-sen Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China. The dataset contains 300 pairs of two clinical modality images. The two modalities are 2D fundus color photography and 3D Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), which are commonly used in clinical fundus examination. We divided all kinds of data into three equal groups, and prepared 100 data pairs for the training process, the preliminary competition process and the final process. For the deep learning algorithm, the 100 training data pairs belong to a small number of samples, so we encourage participants to propose a model suitable for the training of small sample dataset.
GAMMA数据集中的数据包含了所属青光眼分级、黄斑中央凹坐标、以及视杯视盘分割标注。下面将按照三个子任务介绍各种标注的实现过程。
The data in the GAMMA dataset included the respective glaucoma grades, the fovea coordinates, and the mask of the cup and optic disc. The following sections describe the implementation of the various annotations according to three sub-tasks.
任务一:青光眼分级 Task 1: glaucoma grading 各数据的青光眼分级任务金标准由临床记录决定,是根据所有临床检查结果得出的结论。临床检查包括但不限于眼底彩照、眼压测量、OCT、视野检查等。
The ground truth of glaucoma grading task for each data was determined by clinical records and was based on the results of all clinical examinations. Clinical examinations include but are not limited to fundus color photography, intraocular pressure measurement, OCT, visual field examination, etc.
任务二:黄斑中央凹定位 Task 2: fovea localization 各数据的初始黄斑中央凹坐标标注由中国中山大学中山眼科中心4名临床眼科医生手动完成,这四名医生在该领域有平均8年的经验(范围5 - 10年)。所有眼科医生在没有获得任何患者信息或数据中疾病流行情况的情况下,独立对图像进行黄斑中央凹坐标的十字定位。随后,4名医生标注的结果汇总给一个更高级的医生(在青光眼领域有10多年经验)进行融合,高级医生会检查4个标注结果,并对其进行求取平均值或微调等操作。
The initial fovea coordinate annotation of each data was performed manually by 4 clinical ophthalmologists from Sun Yat-sen Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, China, who had an average of 8 years of experience in the field (range 5-10 years). All ophthalmologists independently located the fovea in the image using a cross marker without having access to any patient information or knowledge of disease prevalence in the data. The results from the 4 ophthalmologists are then fused by a more advanced ophthalmologist (who has more than 10 years of experience in glaucoma), who checks the 4 markers and adjusts such as averaging them or fine-tuning them.
任务三:视杯视盘分割 Task 3: optic disc and cup segmentation 与任务二相似,各数据的初始视杯视盘分割区域标注由中国中山大学中山眼科中心4名临床眼科医生手动完成。这4名医生在没有获得任何患者信息或数据中疾病流行情况的情况下,独立对图像中视盘和视杯区域进行勾勒。随后,4个初始标注结果汇总给任务二中的更高级医生进行融合。视杯视盘分割结果的融合采用多数投票的方式,融合医生检查初始的分割标注,并选择取哪几位医生标注结果的交集作为最终视杯视盘分割金标准。
Similar to Task 2, the annotation of the initial segmentation region of the optic cup and disc for each data was manually annotated by 4 clinical ophthalmologists from Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center of Sun Yat-sen University, China. These 4 physicians independently delineated the optic disc and cup areas in the images without any patient information or disease prevalence in the data. The results of the 4 initial segmentation results were then aggregated by the more senior ophthalmologist in Task 2 for fusion. The fusion of the results of optic cup and optic disc segmentation was conducted by majority voting. The fusion ophthalmologist examined the initial segmentation marks and selected the intersection of the annotated results of several ophthalmologist as the final golden standard for optic cup and disc segmentation.
数据描述Data Introduction/Description
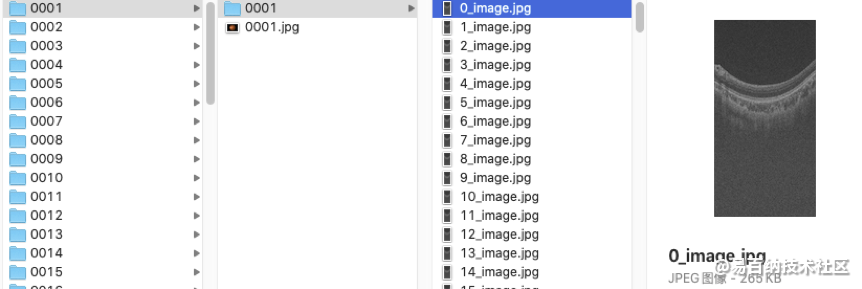
训练集Training set GAMMA21释放的训练数据集包括100个样本0001-0100,每个样本对应一个文件夹(如0001),文件夹中包含该样本的2D眼底彩照数据和3D OCT数据。其中,2D 眼底彩照数据直接存储为0001.jpg,3D OCT数据存储成256个切片图像(0_image.jpg-255_image.jpg),存储文件夹为0001。
The training set released by GAMMA consists of 100 samples 0001 – 0100, each of which corresponds to a folder (e.g. 0001) containing the 2D fundus color image and 3D OCT volume of the sample. Among them, 2D fundus color photo data is directly stored as 0001.jpg, 3D OCT data is stored as 256 sliced images (0_image.jpg-255_image.jpg), and the storage folder is 0001.
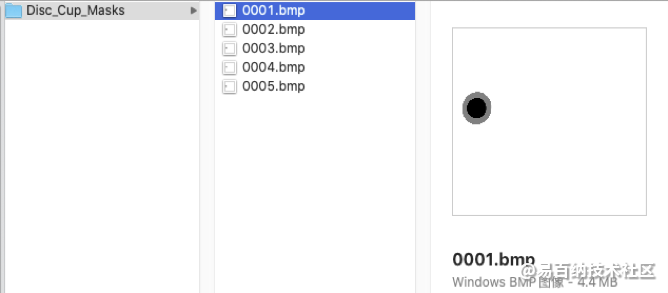
 任务三:视杯视盘分割金标准以bmp图像格式存储,每个样本的眼底图像对应一个视杯视盘分割结果图像。分割结果图像命名与输入的待分割眼底图像命名前缀一致。分割图像中,像素值为0代表视杯区域、像素值为128代表视盘中非视杯区域、像素值为255代表其他区域。所有样本的分割图像存储在Disc_Cup_Masks文件夹中。
任务三:视杯视盘分割金标准以bmp图像格式存储,每个样本的眼底图像对应一个视杯视盘分割结果图像。分割结果图像命名与输入的待分割眼底图像命名前缀一致。分割图像中,像素值为0代表视杯区域、像素值为128代表视盘中非视杯区域、像素值为255代表其他区域。所有样本的分割图像存储在Disc_Cup_Masks文件夹中。
 预赛数据集Preliminary set
预赛数据集中包含100个样本的数据对0101-0200,数据存储格式与训练集中一致。
预赛数据集Preliminary set
预赛数据集中包含100个样本的数据对0101-0200,数据存储格式与训练集中一致。
The dataset of the preliminary competition contains data pairs 0101-0200 of 100 samples, and the data storage format is consistent with that of the training set.
决赛数据集Final set 决赛数据集仅发布给进入决赛的队伍,数据集中包含100个样本的数据对0201-0300。
The final dataset will only be released to the final teams. The dataset contains 100 sample data pairs 0201-0300. The data storage format is consistent with that of the training set.
2 评价指标
2.1 absolute CDR (Cup to Disc Ratio) error(杯盘比错误率)
CDR是杯与盘水平长度,垂直长度和面积的比率。 如果该比率为0.3或更小,则将眼睛视为正常眼睛。 但如果比例超过0.3,眼睛就是异常的威胁。式(1) - (3)定义用于诊断青光眼的各种杯盘比率的计算。


计算方法:
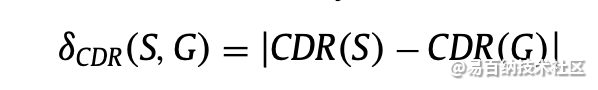
2.2 其他指标
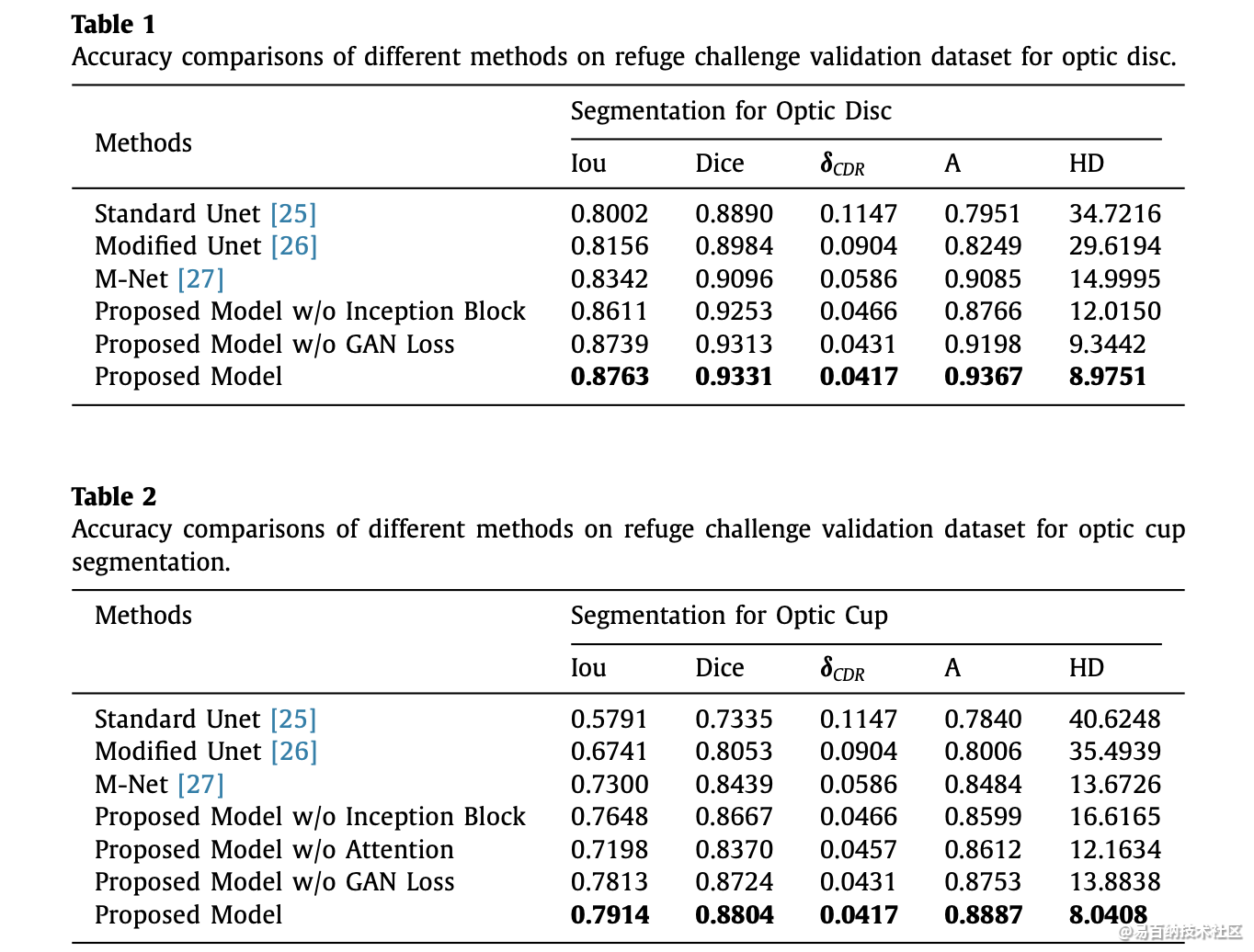 Iou计算:
Iou计算:
在研究目标检测中,IOU的计算是肯定必不可少的。就比如说在R-CNN网络中,正负样本就是按照候选框与真实框之间的IOU值大小进行区分的,可见该细节还是值得单独拎出来写一篇blog的~~ 例如,在R-CNN网络中,我们通过SS(selective search)算法可以实现在每张图片上获得2k左右的候选框,那么如何区分这么多的候选框到底是属于正样本还是负样本呢? 那么IOU这个概念就诞生了~它其实是来源于数学中的集合的概念,用来反应两个集合之间的空间关系;下面是它的计算公式:
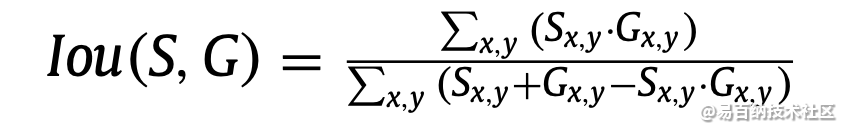
def calc_iou(self, boxes1, boxes2, scope='iou'):
"""calculate ious
Args:
boxes1: 5-D tensor [BATCH_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, BOXES_PER_CELL, 4] ====> 4:(x_center, y_center, w, h)
(2,7,7,2,4)
boxes2: 5-D tensor [BATCH_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, BOXES_PER_CELL, 4] ===> 4:(x_center, y_center, w, h)
(2,7,7,2,4)
Return:
iou: 4-D tensor [BATCH_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, BOXES_PER_CELL] --(2,7,7,2)
"""
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
# transform (x_center, y_center, w, h) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
boxes1_t = tf.stack([boxes1[..., 0] - boxes1[..., 2] / 2.0,
boxes1[..., 1] - boxes1[..., 3] / 2.0,
boxes1[..., 0] + boxes1[..., 2] / 2.0,
boxes1[..., 1] + boxes1[..., 3] / 2.0],
axis=-1) #tf.stack:矩阵拼接
boxes2_t = tf.stack([boxes2[..., 0] - boxes2[..., 2] / 2.0,
boxes2[..., 1] - boxes2[..., 3] / 2.0,
boxes2[..., 0] + boxes2[..., 2] / 2.0,
boxes2[..., 1] + boxes2[..., 3] / 2.0],
axis=-1)
# calculate the left up point & right down point
lu = tf.maximum(boxes1_t[..., :2], boxes2_t[..., :2]) #左上角坐标最大值
rd = tf.minimum(boxes1_t[..., 2:], boxes2_t[..., 2:]) #右下角坐标最小值
# intersection
intersection = tf.maximum(0.0, rd - lu)
inter_square = intersection[..., 0] * intersection[..., 1]
# calculate the boxs1 square and boxs2 square
square1 = boxes1[..., 2] * boxes1[..., 3]
square2 = boxes2[..., 2] * boxes2[..., 3]
union_square = tf.maximum(square1 + square2 - inter_square, 1e-10)
return tf.clip_by_value(inter_square / union_square, 0.0, 1.0) #截断操作,即如果值不在指定的范围里,那么就会进行最大小值截断
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
3 总结
研究不足 1.研究人员不时地考虑了特征的数量以进行分类,但仍然有一些特征可以被考虑用于改进分类器的性能。 2.由于低对比度和圆盘与杯子之间的不可见边界,在大的和小尺寸的视盘和视杯的分割或过度分割被认为是挑战。 3.分类的准确性随着图像数量的增加而降低。 因此,需要改进分类方法来精确地分类正常和异常情况。 4.视网膜血管和周围萎缩的存在降低了分割的性能。 因此,需要改进预处理方法来移除血管并避免作为视盘区域的周围区域。 5.对视杯的分割工作较少。 因此,需要改进的视杯分割方法来诊断青光眼。 6.由于复杂性增加和精度降低,所有诊断参数未同时考虑在内。 7.由于复杂性增加,有限的方法已用于融合视盘和视杯的分割。 8.现有的分割和分类方法缺乏对大规模数据集进行临床评估的测试。
发现 1.红色通道更适合于视盘分割,因为与其他通道相比,该通道中的视盘具有清晰的外观。 2.与其他通道相比,由于该通道的高对比度,绿色通道更适合于视杯的分割。 3.形态学方法和各种滤波器用于预处理视网膜图像以去除图像中存在的血管,这可能进一步造成分割困难。而且,从讨论中可以分析每种方法都有自己的方法。 表4中给出的优点和缺点取决于某些因素。此外,可以分析这种分类器对分类没有很好的分类。 每种技术都有其自身的优点和缺点,如表5所示,这取决于某些因素,如输入数量,输入质量和分类时间的可用性。 但是已经发现,在这种情况下,由于最大精度,SVM分类器是常用的。
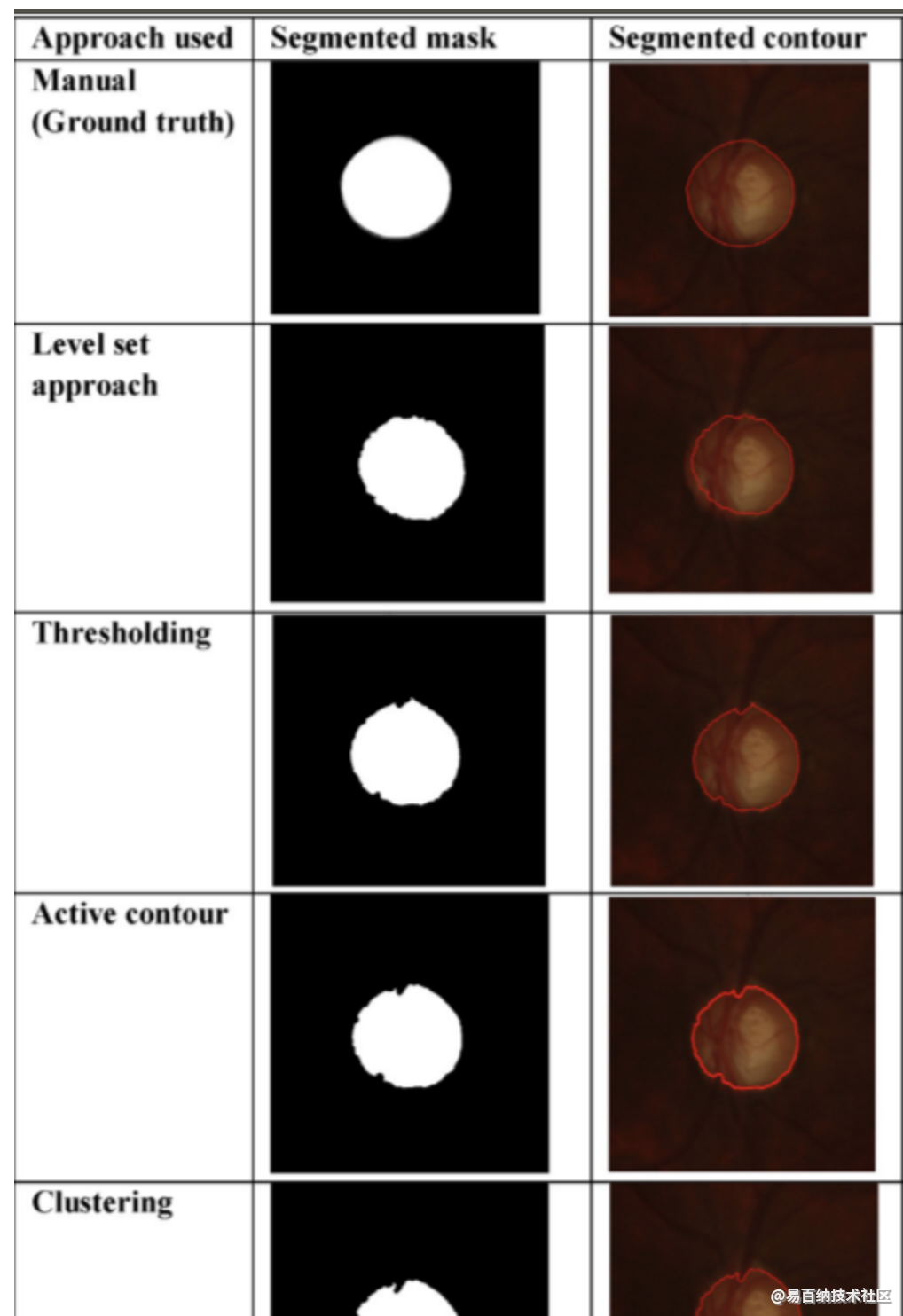
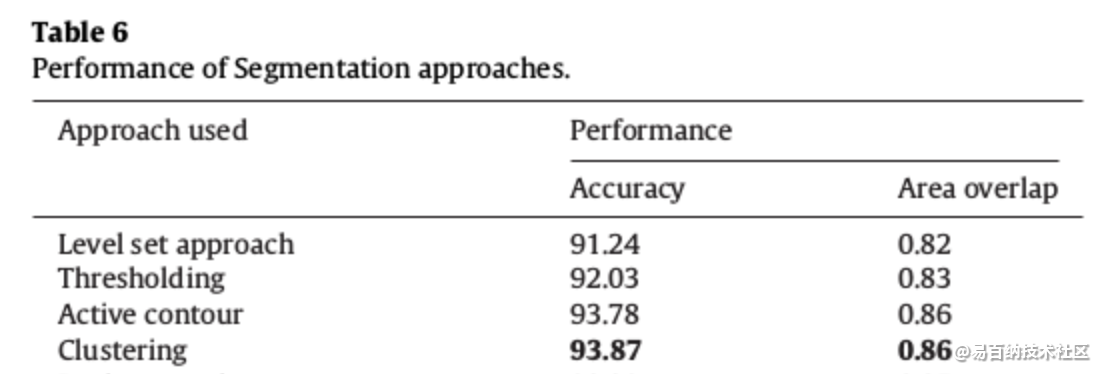
除了第6.2节中给出的结果外,我们还评估了我们数据集中某些现有技术方法的性能,如图5和表6所示。基于主观分析,我们得出结论:Clustering聚类得到最大准确度,因此可以进一步扩展分割。与主观/定性分析相似,客观/定量分析表明基于Clustering聚类的方法优于其他现有技术方法,如表6所示。
- 分享
- 举报
 暂无数据
暂无数据-
浏览量:14429次2021-05-04 20:16:03
-
浏览量:13497次2021-07-05 09:47:30
-
浏览量:9298次2021-06-21 11:49:58
-
浏览量:6840次2021-05-04 20:17:10
-
浏览量:6641次2021-06-07 09:26:53
-
浏览量:7562次2021-07-19 17:08:40
-
浏览量:8889次2021-07-19 17:09:44
-
浏览量:7445次2021-07-19 17:10:27
-
浏览量:12966次2021-05-12 12:35:30
-
浏览量:13053次2021-05-11 15:08:10
-
浏览量:157次2023-08-30 15:28:02
-
浏览量:15964次2021-07-16 12:56:10
-
浏览量:6216次2021-05-17 16:48:29
-
浏览量:13526次2021-07-08 09:43:47
-
浏览量:7357次2021-04-29 12:46:50
-
浏览量:353次2023-07-24 11:00:24
-
浏览量:5146次2021-06-21 11:50:25
-
浏览量:9654次2021-05-24 15:12:00
-
浏览量:1629次2023-02-14 14:48:11
-
广告/SPAM
-
恶意灌水
-
违规内容
-
文不对题
-
重复发帖
这把我C





 微信支付
微信支付举报类型
- 内容涉黄/赌/毒
- 内容侵权/抄袭
- 政治相关
- 涉嫌广告
- 侮辱谩骂
- 其他
详细说明



 微信扫码分享
微信扫码分享 QQ好友
QQ好友





